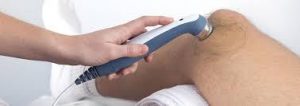
 Therapeutic ultrasound is used primarily for two different effects: the deep heating treatment and non-thermal uses.
Therapeutic ultrasound is used primarily for two different effects: the deep heating treatment and non-thermal uses.
Deep Heating Effects
Ultrasound is often used to provide deep heating to soft tissue structures in the body. Deep heating tendons, muscles or ligaments increases circulation to those tissues, which is thought to help the healing process. Increasing tissue temperature with ultrasound is also used to help decrease pain.
Deep heating can be used to increase the “stretchiness” of muscles and tendons that may be tight. For example if you have shoulder pain and have been diagnosed with a frozen shoulder, your doctor may use ultrasound to help improve the extensibility of the tissues around your shoulder prior to performing an adjustment or range of motion exercises.
Non-Thermal Effects (Cavitation)
Ultrasound introduces energy into the body. This energy causes microscopic gas bubbles around your tissues to expand and contract rapidly, a process called cavitation. The expansion and contraction of these bubbles help speed cellular processes and improves healing of injured tissue.
Ultrasound is very effective on acute injuries such as injured discs, pulled or strained muscles, shin splints, inflamed aching joints, and more.
